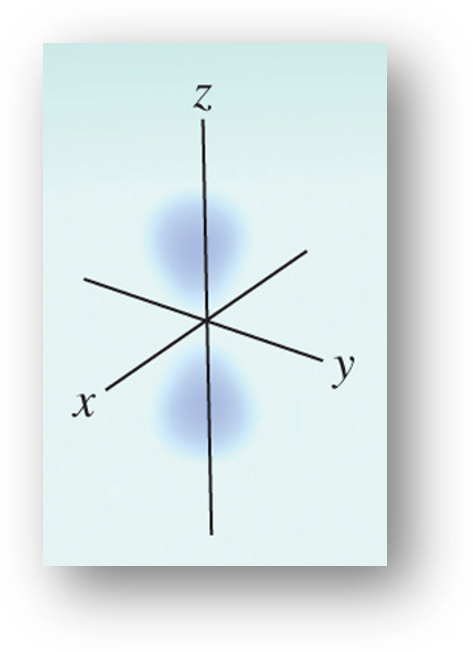
3.5 Schrodinger Equation
Erwin Schrödinger derived a complex mathematical formula to incorporate the wave and particle characteristics of electrons. Wave behavior is described with the wavefunction, Ψ. The probability of finding an electron in a certain area of space is proportional to Ψ2 and is called electron density. Quantum Mechanics defines the region where the electron is most likely to be at a given time
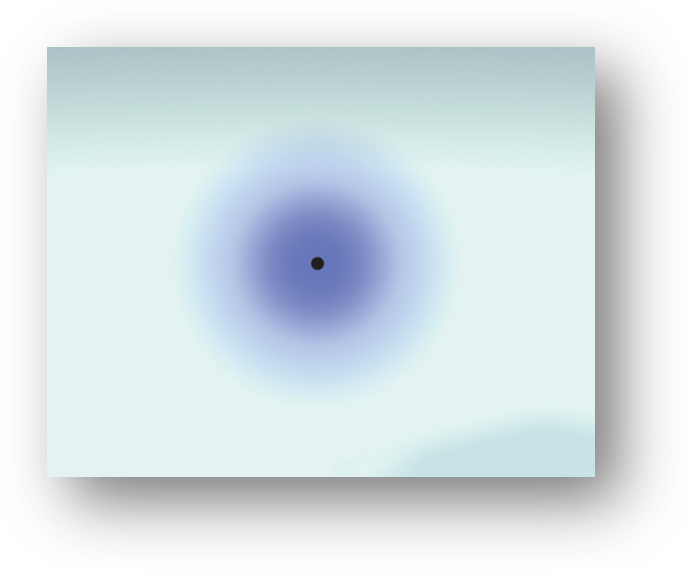

The Schrödinger equation specifies possible energy states an electron can occupy in a hydrogen atom. The energy states and wave functions are characterized by a set of quantum numbers. Instead of referring to orbits as in the Bohr model, quantum numbers and wave functions describe atomic orbitals.