Chapter 4 Bonding and Molecular Geometry
A compound is a substance composed of two or more elements combined in a specific ratio and held together by chemical bonds. Ionic bonding refers to the electrostatic attraction that holds oppositely charged ions together in an ionic compound.
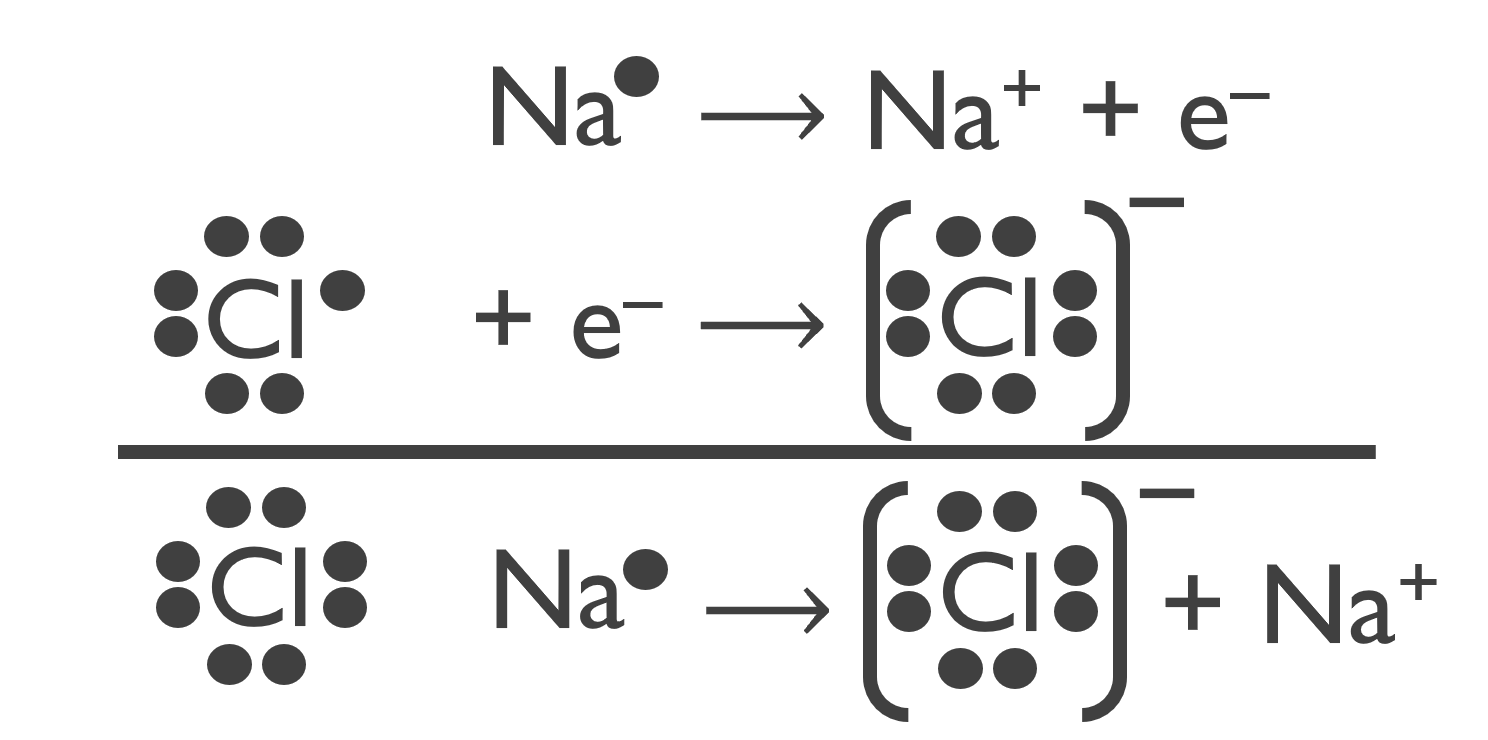
Figure 4.1: The attraction between the cation and anion draws them together to form NaCl. The resulting electrically neutral compound, sodium chloride, is represented with the chemical formula NaCl.
The chemical formula, or simply formula, of an ionic compound denotes the constituent elements and the ratio in which they combine. Ionic compounds typically have a metal ion and a non–metal ion to form the compound.
Elements can be categorized as metals, nonmetals, or metalloids.
Metals (teal) are good conductors of heat and electricity.
- solids (except mercury – a liquid)
- ductile (can be drawn into wires)
- malleable (can be rolled into sheets)
Nonmetals (pink) are poor conductors of heat or electricity. (graphite is the one exception) Occur in all physical states.
Metalloids (purple) have intermediate properties. Boron, silicon, germanium, arsenic, antimony, tellurium, (astatine) They exhibit metallic and nonmetallic properties:
- Conduct electricity (not as well as metals).
- Look like metals (shiny).
- semiconductors.
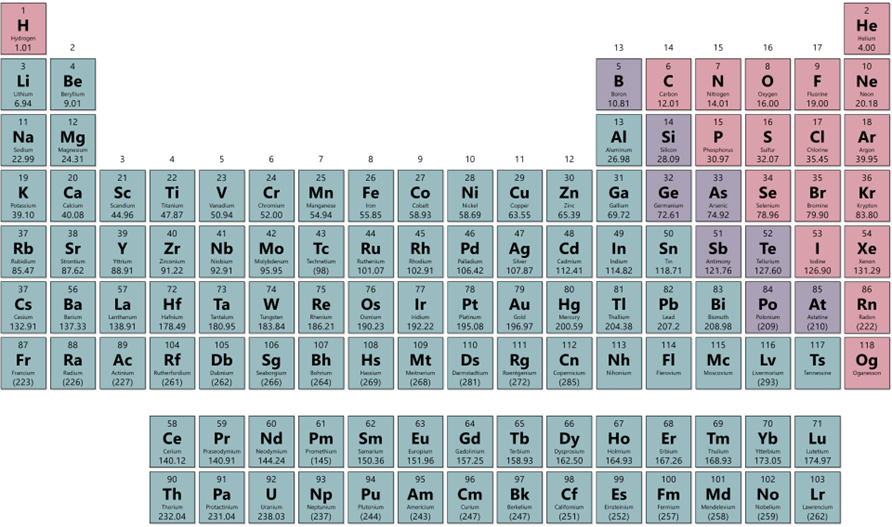
Figure 4.2: Metals (teal), Non-metals (pink) and metalloids (purple)